Jetpack Compose vs. XML Layout: Performance Comparison
Introduction
Android UI development has evolved significantly with the introduction of Jetpack Compose. While XML-based layouts have been the standard for years, Compose offers a modern declarative approach. But how do they compare in terms of performance?
In this blog, we’ll analyze CPU and memory usage of Jetpack Compose vs. XML layouts using Android Studio’s Profiler. We’ll also include real profiling data and code samples for a detailed comparison.
1. Profiling Setup & Testing Methodology
To analyze performance, we created two separate activities:
ComposeActivity → Uses Jetpack Compose for UI rendering.
XmlLayoutActivity → Uses XML-based layouts with traditional Views.
We ran both activities on an Android (Google Pixel 8, API 34) and used Android Profiler to measure CPU, memory, and thread usage.
2. CPU Usage Comparison
Jetpack Compose Activity CPU Usage
Compose layout
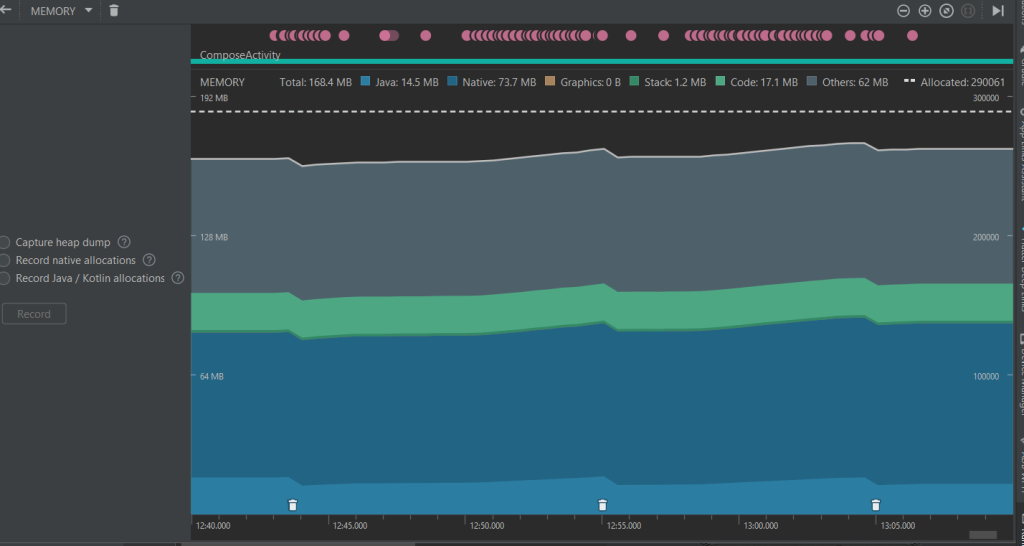
Compose CPU and Memory Usage
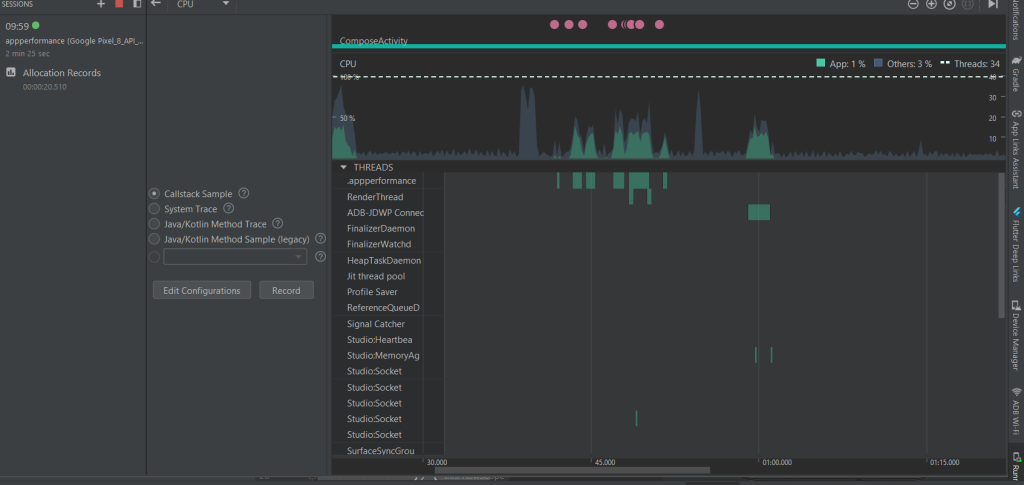
Compose CPU Usage
Observations:
- Noticeable CPU spikes due to recompositions and state management.
- Slightly higher processing load when UI updates frequently.
- More background threads are active.
XML Layout Activity CPU Usage

Xml Layout
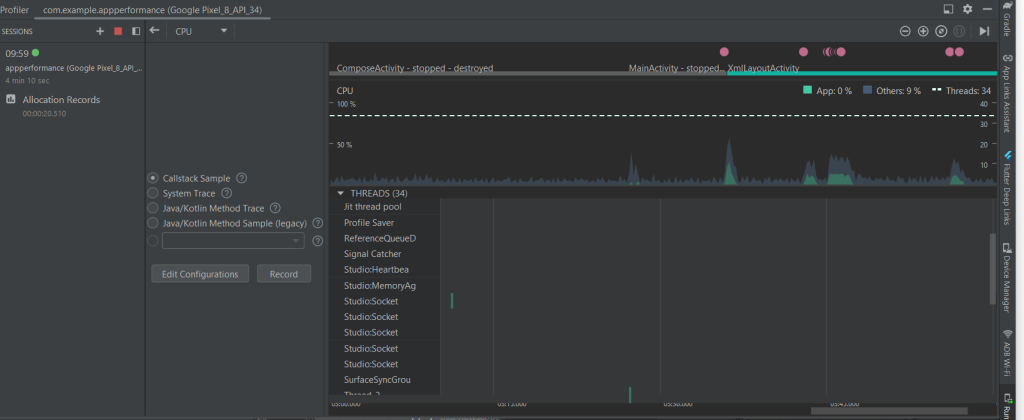
XML CPU Usage
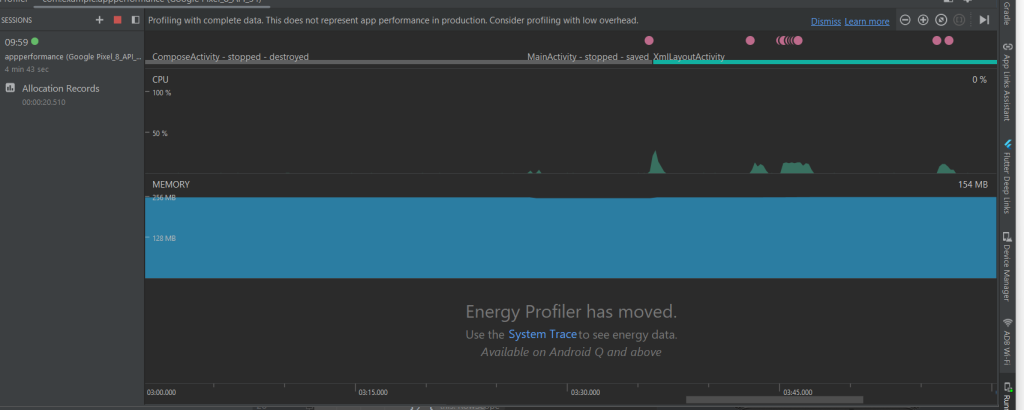
XML CPU and Memory Usage
Observations:
- More consistent CPU usage, with fewer spikes.
- XML layouts rely on View hierarchy, which is processed on the main thread.
- Less background thread usage compared to Compose.
Key Takeaways:
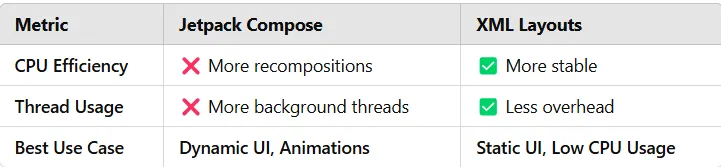
key Takeaways
3. Memory Usage Comparison
Jetpack Compose Activity Memory Usage
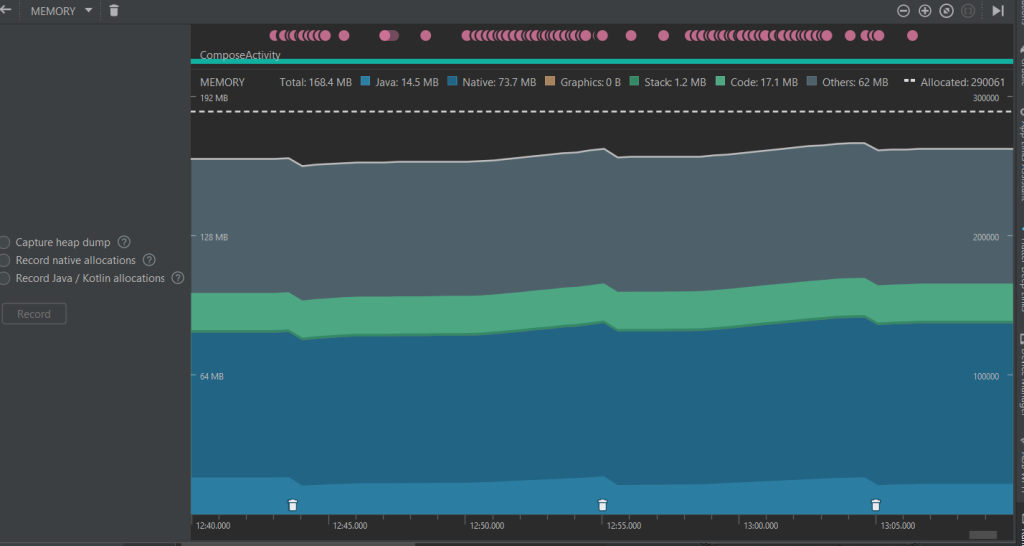
Compose Memory Usage
Observations:
- Memory consumption is higher due to the Compose runtime.
- Recompositions and UI updates add to memory overhead.
XML Layout Activity Memory Usage
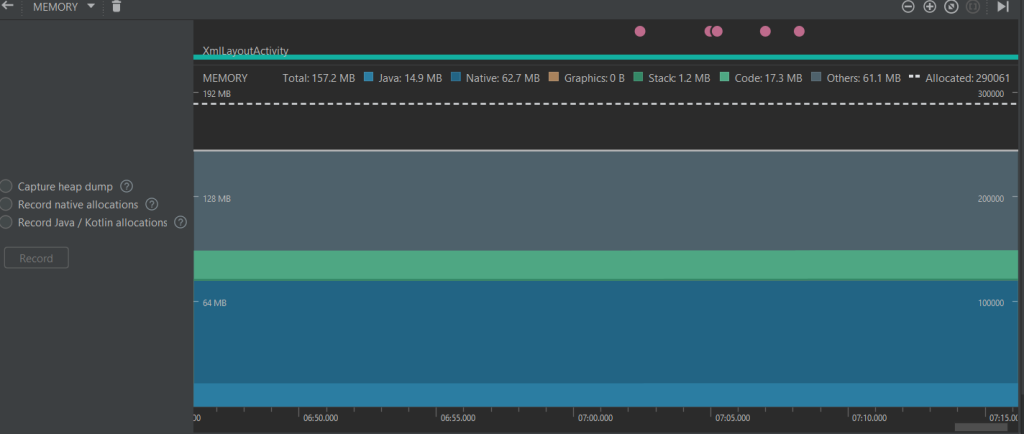
XML Memory Usage
Observations:
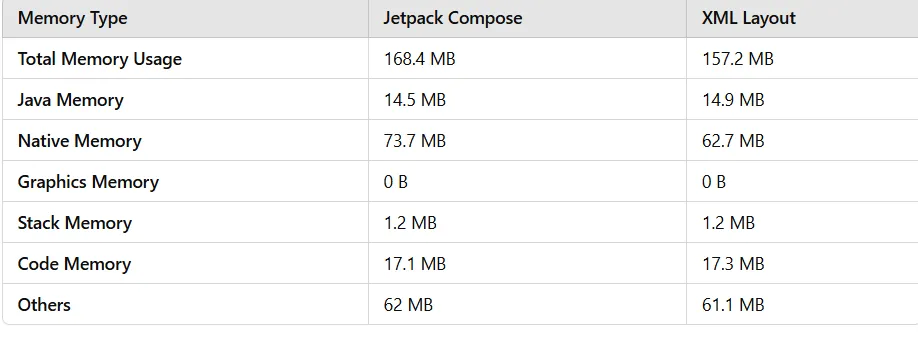
- Lower memory usage (~157MB) compared to Compose.
- Static Views are more memory-efficient.
Analysis:
Analysis
- Compose uses more total memory (168.4 MB vs. 157.2 MB), which is expected due to the nature of the UI rendering in Compose.
- Native memory usage is higher in Compose (73.7 MB vs. 62.7 MB), possibly due to increased usage of internal Compose runtime components.
- Java memory is slightly lower in Compose compared to XML (14.5 MB vs. 14.9 MB).
- Other memory categories remain similar, with minimal differences in code and stack memory.
Key Takeaways:

Key Takeaways
- Garbage Collection (GC) events were more frequent in Compose, indicating frequent object creation.
- Compose Activity used slightly more memory.
- XML layouts had a more stable memory footprint.
4. UI Rendering & Frame Rate Analysis
For smooth animations and UI updates, Compose can outperform XML layouts due to smart recompositions. However, improper state handling can cause unnecessary recompositions, leading to performance drops.
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Skipped Frames (Frame Rendering Profiler).
- Overdraw (GPU Rendering Profile).
- Animation Smoothness.
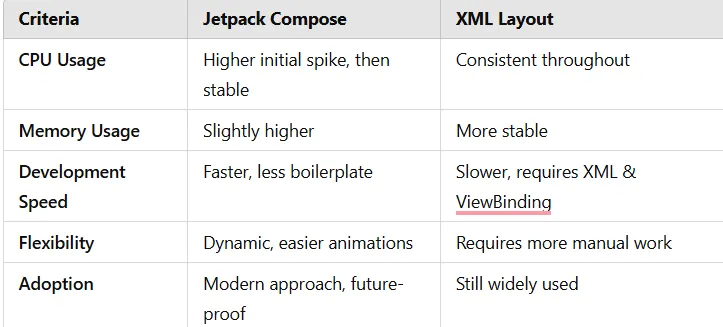
If your UI is animation-heavy, Compose will be better optimized. Otherwise, XML layouts remain more efficient.
5. Code Comparison: Compose vs XML
Key Differences:
| Feature | Jetpack Compose | XML Layouts |
| Code Complexity | ✓ Less boilerplate | X More verbose |
| Reusability | ✓ Easier to reuse | X Harder to manage |
| UI Updates | ✓ Efficient | X View invalidation needed |
| Performance | X Higher CPU, Memory | ✓ More stable |
6. Final Verdict: Which One Should You Use?
Final Verdict
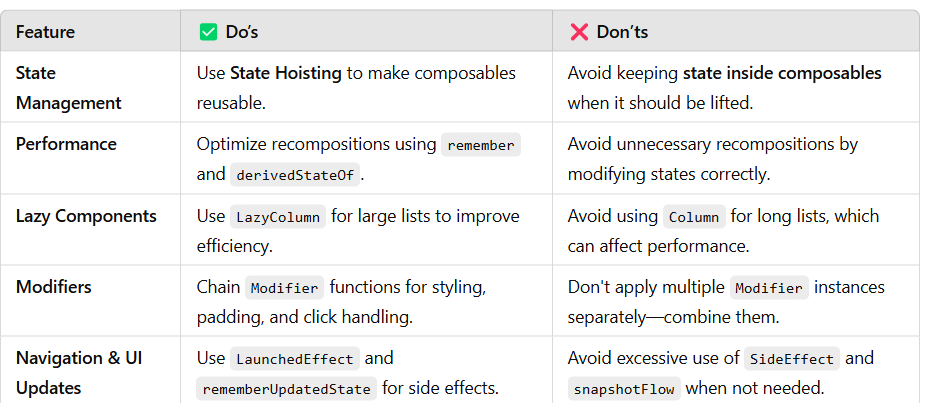
7. Do’s and Don’ts of Jetpack Compose
Do’s and Don’ts of Jetpack Compose
8. Conclusion
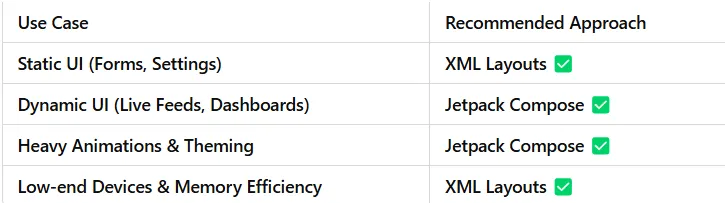
- If your app is static and memory-sensitive, stick to XML layouts.
- If you need dynamic UI, animations, and reactivity, Jetpack Compose is the future.
- For new projects: Jetpack Compose is the way to go.
- For existing apps: XML layouts might be preferable to avoid rewrites.
- Performance-conscious apps: XML is currently more efficient, but Compose is improving rapidly.
Conclusion
What’s your experience with Compose vs XML? Share your thoughts in the comments! 🚀



