Unmasking Tab-Nabbing: Navigating Web Security Threats
As businesses move towards achieving a complete digital transformation, their need for the right digital skills and expertise only increases. In today’s speedy-paced virtual world, it’s not unusual to juggle multiple browser tabs whilst multitasking. However, this apparently harmless dependency can expose users to a lesser-recognized cybersecurity danger: TAB-NABBING!
What Is Tab-Nabbing?
Tab-nabbing (also known as tabjacking) is a sneaky sort of phishing assault that takes advantage of customers who leave multiple tabs open in their browsers. Introduced with the aid of Aza Raskin in 2010, tab-nabbing entails replacing an inactive browser tab with a fraudulent web page designed to imitate a valid website online. The purpose is to trick users into entering touchy data like login credentials or monetary information without figuring out the page has been modified.

Tab-Nabbing
- Tab-nabbing exploits the idea that once a browser tab is open, its contents remain unaltered.
- This false impression offers attackers an opportunity to set up a malicious script.
- When users become inactive or distracted, the script quietly adjusts the content material of the tab to display a phishing web page.
- Once the user returns to the tab, they are satisfied they are still on a valid page, unaware that their private information is at risk.
Understanding the Same-Origin Policy (SOP)
To hold close to how tab-nabbing works, it’s critical to recognize an essential web security concept—the Same-Origin Policy (SOP). SOP is like a digital gatekeeper that forestalls websites from interacting with each other until they share the same foundation (area, protocol, and port). For instance, Facebook can not get the right of entry to records from a tab open to Google inside the equal browser window, ensuring privacy between special web apps.

SOP in tabs
However, regardless of the SOP in place, vulnerabilities nonetheless exist. Attackers can exploit those by way of the usage of a trick referred to as “window control.” For instance, Site A can manipulate Site B’s window by taking control of its window object, permitting an attacker to redirect the user from Site B to any URL they pick, often a malicious internet site.
Read More: The Impact of Continuous Testing- How Organizations Transform Their Testing from Reactive to Innovative
How Tab-Nabbing Works
Here’s how regular tab-nabbing assaults unfold:
1. Malicious Page Opens a New Tab
A malicious website uses JavaScript to open a new tab in your browser. The new tab appears harmless or blank, so you ignore it.
While you are busy, the attacker changes the tab’s content to a phishing page, like a fake login screen. When you return to the tab, it looks legitimate. You enter sensitive information, which the attacker steals.
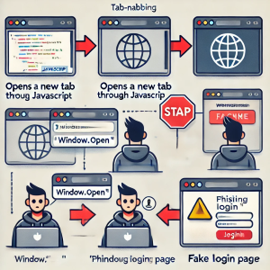
How tab-nabbing works
2. Reverse Tab-Nabbing
In this transformation, it’s a valid internet site that opens a brand new tab. However, the attacker manipulates the opener window using `window. Opener` and swaps it with a malicious site. The consumer returns to the authentic tab, wondering whether they’re nonetheless dependent on the web page, whilst, in fact, it’s been replaced.
In each instance, the attacker is predicated on the user’s inattentiveness and trust in the authenticity of browser tabs, making these assaults specifically effective.
Guarding Against Tab-Nabbing
While tab-nabbing poses a real risk, there are realistic steps each user and developer can take to decrease the chance:
- Keep Software Updated:
Ensure that your browser and operating gadget are continually up to date with cutting-edge variations. Developers regularly launch safety patches to address vulnerabilities that attackers should take advantage of.
- Be Cautious with Links:
Think twice before clicking on hyperlinks, particularly from unusual or untrusted sources. Malicious websites often depend on social engineering techniques to convince users to visit fraudulent pages.
- Verify URLs:
Always double-test the URL in the browser’s address bar before entering any private statistics. Make certain the URL suits the valid site you are supposed to visit, as phishing sites regularly have slightly altered URLs to mislead users.
- Use Browser Extensions:
Install browser extensions that help block malicious scripts and defend against phishing assaults. This equipment provides a further layer of security at the same time as surfing.
- Implement `rel=noopener` for Developers:
Website developers can defend customers from tab-nabbing by way of adding the `rel=noopener` attribute to external hyperlinks. This prevents malicious sites from manipulating the opener window and accessing the unique web page that opened them.
By staying informed about today’s threats, inclusive of tab-nabbing, and adopting satisfactory safety practices, you may drastically reduce the dangers and browse the internet with extra self-belief. Remember, your online safety is on your fingers—live vigilantly and defend yourself from unseen virtual threats.
Keeping their requirements at the center of it all, TO THE NEW offers a comprehensive set of manual as well as automated testing services. We aim to transform the traditional Quality Assurance to Quality Engineering by leveraging technology catering to CI/CD & Agile environments.
Happy Testing!
Stay online safe:)

