Unraveling the Power of gRPC: A Comprehensive Guide to the Protocol
What is gRPC?
gRPC, which stands for gRPC Remote Procedure Call, is an open-source RPC (Remote Procedure Call) framework developed by Google. It leverages the HTTP/2 protocol for transport and Protocol Buffers as the interface description language. gRPC is designed to provide a high-performance, language-agnostic framework for building efficient and scalable distributed systems.
Key Features of gRPC
Language Agnostic: gRPC supports many programming languages, making it a versatile choice for building microservices in multilingual environments. Supported languages include but are not limited to Java, Python, Go, C++, C#, and more.
IDL with Protocol Buffers: Interface Definition Language (IDL) is crucial for defining the structure of services. gRPC uses Protocol Buffers (protobuf) as its IDL, a language-agnostic binary serialization format. Protobuf allows for easy definitions of service methods, message types, and more.
Bidirectional Streaming: One of the standout features of gRPC is its support for bidirectional streaming. This enables multiple clients and servers to send a stream of messages concurrently. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where real-time updates are crucial.
HTTP/2 Protocol: gRPC utilizes the HTTP/2 protocol for communication between clients and servers. This brings advantages like multiplexing, header compression, and asynchronous communication, contributing to improved efficiency and reduced latency.
Pluggable and Extensible: gRPC is designed with extensibility in mind. It allows developers to plug in different authentication mechanisms, load-balancing strategies, and more. This flexibility makes it suitable for various deployment scenarios.
Use Cases of gRPC:
Microservices Architecture: gRPC is well-suited for microservices architectures where services must communicate efficiently in a distributed environment. Its small payload and high-performance characteristics make it an ideal choice for building microservices.
Real-time Applications:The bidirectional streaming capability of gRPC makes it suitable for real-time applications such as chat applications, online gaming, and collaborative editing tools.
Cross-language Communication: The language-agnostic nature of gRPC facilitates communication between services developed in different programming languages, promoting interoperability in diverse tech stacks.
High-Performance APIs: For scenarios where low latency and high performance are crucial, gRPC’s use of HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers can significantly enhance the efficiency of API communication.
Conclusion
Creating a gRPC service in Node.js involves several steps:
Defining the service using Protocol Buffers (protobuf), implementing the service in Node.js, and writing a client to call the service.
Here’s a step-by-step guide
Step 1: Install gRPC and Protocol Buffers
Step 2: Define the gRPC Service
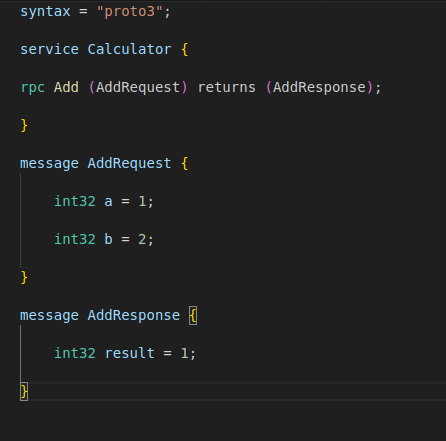
Protobuf
Step 3: Implement the gRPC Server
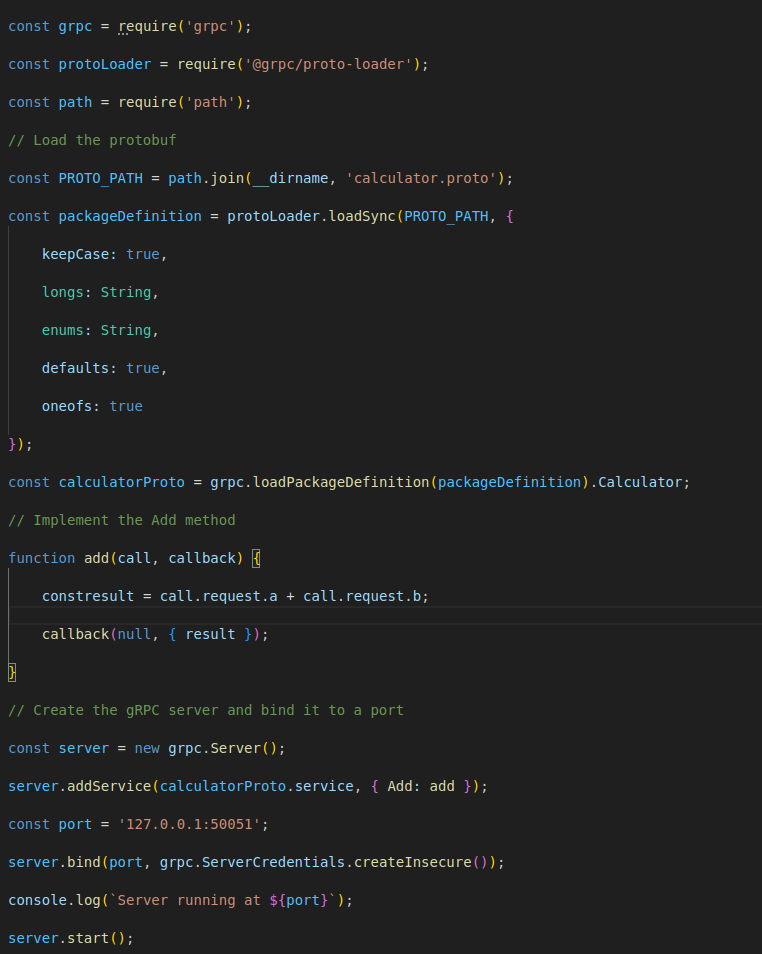
server.js
Step 4: Implement the gRPC Client
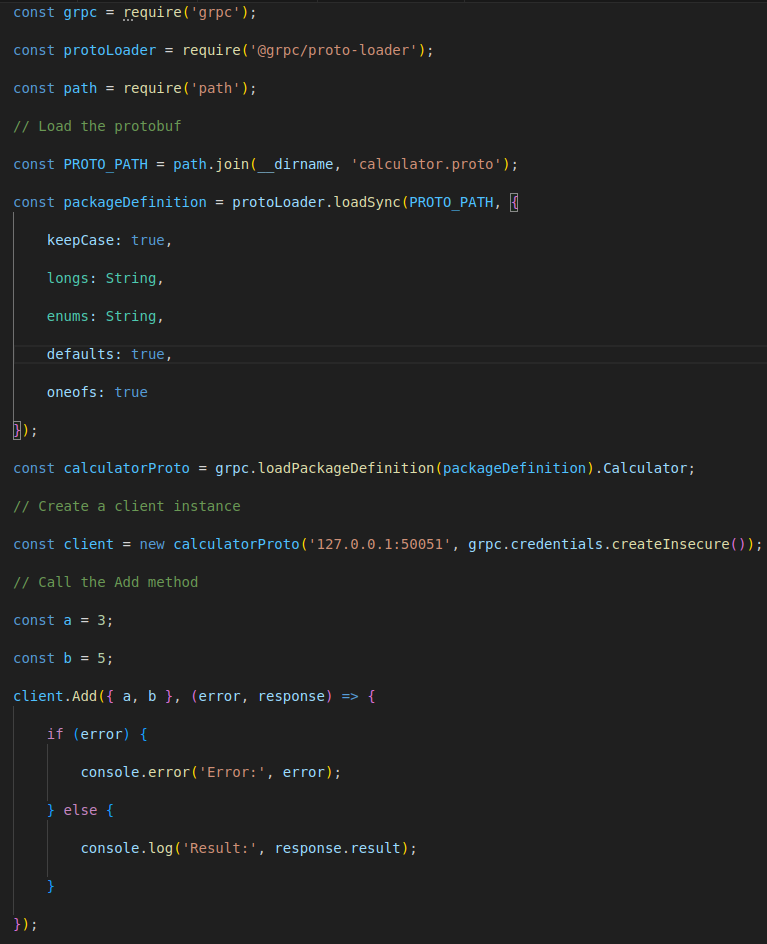
client.js
Step 5: Run the Server and Client
node server.js
node client.js
Result: 8

